Investment Approach
1031 Exchange Investment Options
Looking for information to help you explore 1031 exchange investment options? Our handy, educational 1031 exchange guide is here for you.
If you are one of the many Americans who manage investment real estate, you know that some assets need to be sold from time-to-time. This move may be motivated by underperformance, a desire to diversify your holdings, discover more attractive alternatives elsewhere, or absolve oneself of property management duties.
Either way, you can expect one commonality: paying taxes on your capital gains. But what if I told you that a convenient tool outlined in the Internal Revenue Code allows you to defer the capital gains taxes on the sale of investment properties?
I would be referring to the 1031 exchange, which will enable you to retain funds within your portfolio rather than surrendering them to the IRS. In this guide, I’ll explain and help you understand the nuances of this powerful tax deferral tool before you explore the 1031 exchange investment options available to you.
Understanding 1031 Exchange Investment Options
Understanding 1031 Exchange Investment Options
To explore your 1031 exchange investment options, it’s essential that you possess a foundational understanding of both capital gains taxes and the intricacies of 1031 exchanges.
Usually, when you sell an investment property, you are expected to pay a percentage of the profits, also known as capital gains, from the sale to the IRS. This conventional approach poses a challenge for investors, as it has the potential to diminish their overall profits significantly.

Understanding Capital Gains Taxes
The percentage rate of capital gains depends on various factors, including:
- The Holding Period: This is the duration you have held the real estate property. These are broken down into short-term and long-term holding periods and are taxed at different rates. Also, while there is no clearly defined minimum time that a property must be held before it is sold and used in a 1031 exchange, it’s generally agreed upon that you need to hold onto a property for at least a year to obtain long-term gain treatment.
- Income Level: Your overall income will significantly determine your capital gains tax rate. Higher-income individuals can expect higher capital gains tax rates and may also be subject to the Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT).
- Filing Status: Your filing status (single, married, filing jointly, head of household, etc.) can impact your capital gains tax rate.
- State Taxes: State taxes may or may not be favorable to long-term capital gains, depending on the state. State tax rates and rules vary.
This rate will affect the exact amount of your capital gains tax liability.
For example, let’s say you purchased a duplex for $500,000 and have been renting it out to tenants for ten years. In that time, the property’s value increased to $750,000. When you decide to sell that property, you will be expected to pay your determined rate as a percentage of that profit as capital gains tax.
If you’re a high-income earner in California, your capital gains tax rate could be as high as 37.1% (23.8% federal + 13.3% state). That means you’ll owe 37.1% of your $250,000 tax profit!
Let’s visualize it.
| Calculating Capital Gains Tax on the Sale of an Investment Property | |||
| Component | Amount | Rate | Tax Calculation |
| Purchase Price | $500,000 | – | – |
| Sale Price | $750,000 | – | – |
| Capital Gain | $250,000 | – | – |
| Federal Capital Gains Tax | $250,000 | 20% (if held > 1 yr) | $50,000 |
| Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT) | $250,000 | 3.8% | $9,500 |
| State Capital Gains Tax | $250,000 | 13.3% | $33,250 |
| Total Capital Gains Tax Owed | – | 37.1% | $92,750 |
| Net Proceeds | $657,250 | – | $75,000 – $92,750 |
As you can see, if you were to pay the capital gains taxes in this scenario, you would be losing over a third of your profit in taxes!
Luckily, 1031 exchanges offer investors the opportunity to defer these capital gains taxes by reinvesting them into a replacement property, keeping your profits within your portfolio.
Understanding 1031 Exchanges
1031 exchanges, also known as like-kind exchanges by some, is a provision outlined within the United States Internal Revenue Code (Section 1031)1. It allows investors to defer the capital gains taxes on the sale of specific real estate properties as long as the proceeds from the sale are invested into another qualifying property.
The idea is to incentivize the continued investment and circulation of capital in the real estate market. As a bonus, it gives investors like you the unique opportunity to keep money within their investment portfolios and increase purchasing power when acquiring new investment properties.
How a 1031 Exchange Works
- Qualifying Properties: Both the property you’re selling (relinquished property) and the property(s) you’re acquiring through the 1031 exchange (replacement property) must be held for investment purposes. You cannot use primary or secondary residences for either.
- Types of Qualifying Properties:
- Multifamily Rentals
- Single-Family Rentals
- Raw Land
- Retail Shopping Centers
- Office Buildings
- Industrial Facilities
- Storage Facilities
- Types of Qualifying Properties:
- Qualified Intermediaries (QIs): Direct receipt of sales proceeds from the relinquished property is prohibited. Instead, employing a Qualified Intermediary (QI), a third party responsible for holding the proceeds, facilitating the exchange, and ensuring compliance with regulations is mandatory.
- Identification Periods: 1031 exchanges must occur with tight deadlines, and typically, extensions are not allowed except under rare circumstances. There are two windows to be aware of that run concurrently.
- 45-Day Identification Period: After the relinquished property is sold, you must identify all potential replacement properties within 45 calendar days.
- 180-Day Identification Period: You have a total of 180 calendar days to complete the entire 1031 exchange process from the day the relinquished property is sold.
- 45-Day Identification Period: After the relinquished property is sold, you must identify all potential replacement properties within 45 calendar days.
- Reinvestment of Equity: All net proceeds from the sale of the relinquished property must be used to purchase any replacement properties. If there is any cash or debt relief involved, it is treated by the IRS as taxable “boot.”
- Tax Deferral: The capital gains tax from the sale of the relinquished property is deferred until the replacement property is sold without initiating another 1031 exchange. In theory, this implies the potential to continuously defer capital gains taxes indefinitely as long as you consistently participate in 1031 exchanges.
- Multiple Properties: While 1031 exchanges are commonly used for 1:1 property exchanges, exchanging one property for multiple is possible by using the 1031 exchange 200 rule. This rule stipulates that the replacement properties do not exceed 200% of the value of the relinquished property.
Benefits of a 1031 Exchange
Since they provide the basis for a tax-deferred strategy to optimize real estate investment portfolios, 1031 exchanges offer investors many potential benefits. Here are some of the most noteworthy ones.
- Tax Deferral: The primary benefit of 1031 exchanges that I’ve been harping on over the last 1000 words. 1031 exchanges allow investors to defer capital gains tax on the sale of their relinquished property, and they can theoretically continue to do so until they sell a property without exchanging.
- Portfolio Diversification: Utilizing 1031 exchanges enables investors to broaden their investment portfolios strategically. This is possible because 1031 exchanges can reallocate investments across various property types, locations, or markets without triggering immediate tax consequences.
- Wealth Accumulation: Deferring taxes allows investors to retain larger portions of their portfolios when selling qualifying real estate.
- Leverage of Equity: 1031 exchanges allow investors to utilize the equity from the sale of the relinquished property to acquire more numerous or valuable properties, potentially increasing income generation and property appreciation.
- Estate Planning Benefits: When an investor with a 1031 exchange property passes away, the property’s cost basis is “stepped up” for their heirs. This can potentially minimize the tax impact when the heirs eventually sell the property, and they may even be able to use a 1031 exchange on the property.
- Business Expansion: 1031 exchanges allow investors to expand or consolidate real estate holdings without being on the hook for immediate capital gains tax liabilities.
- Risk Mitigation: Investors can use 1031 exchanges to fine-tune their investment strategy in response to economic factors or market conditions.
- Cash Flow Improvement: Investors can replace properties with those that may provide the opportunity for higher income potential, which may lead to increased cash flow. This is great for investors looking to increase their “passive” income streams.
- Preservation of Equity: Because 1031 exchanges defer capital gains taxes, they allow investors to maintain the full equity of their property by reinvesting it.
Potential Concerns of a 1031 Exchange
- Strict Timelines: 1031 exchanges involve rigid timelines that must be followed or risk disqualification of the exchange and leaving you on the hook for capital gains taxes. Factors to consider include the 45-day rule and the 180-day rule. Meeting these deadlines can be challenging for even seasoned real estate investors, especially in competitive or evolving real estate markets.
- Identification Rules: Identification rules such as the 200 rule can add even more complexity to an already complicated process.
- Market Conditions: Market conditions and other economic factors can significantly impact the pricing and availability of replacement properties. Finding suitable properties within the strict timelines that align with your specific investment goals may be challenging.
- Limited Property Options: Since replacement properties are required to be a like-kind, the options are more limited than they would be otherwise, making it difficult to find suitable replacement properties in time to complete the exchange.
- Financing Challenges: Securing loans to cover the remaining expenses of the replacement property involves engaging with lenders. Lenders typically have strict criteria for loan approval, and any delays in the financing process may pose a risk to the success of the 1031 exchange.
- Boot Issues: Receiving any cash or paying off any debt with money used to purchase the replacement property may trigger taxable events. You must carefully manage the transaction to avoid receiving any unintentional boot and incurring tax liabilities.
- Uncertainty of Future Tax Laws: Tax laws are always subject to change, and the future of legislative developments is difficult to predict. Changes in tax codes and laws could impact the benefits and rules of 1031 exchanges.
- Complexity and Professional Fees: In addition to QIs, navigating the complexities of a 1031 exchange may require seeking counsel from tax professionals and legal experts. They may require fees to use their services that add to the transaction cost.
Understand that these factors are all provided to give you a broad understanding of 1031 exchanges. It’s crucial to recognize that the benefits and concerns are context-dependent. Additionally, every investment strategy comes with inherent risks, and success is not assured, much like any other investment.
Always seek advice from your financial advisor before embarking on a new investment strategy to ensure informed decision-making.
A 1031 Exchange in Action
Now that you’ve gained a clearer insight into the concept, workings, and both the advantages and potential challenges of a 1031 exchange, let’s explore the substantial impact this strategy can have.
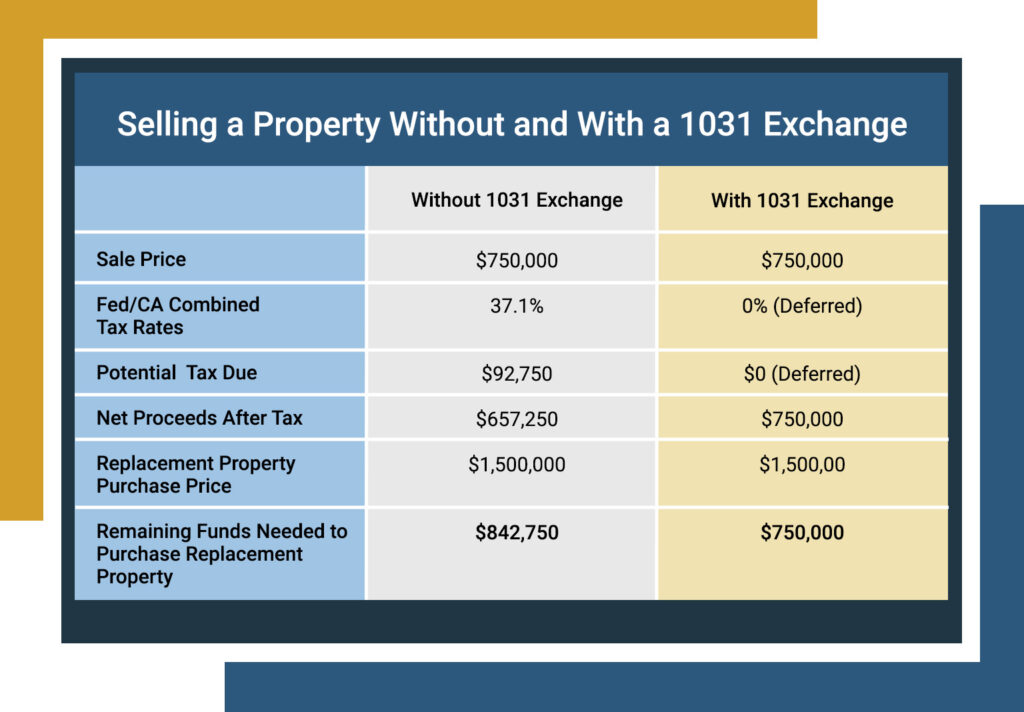
Let’s build on the example from earlier. You’ve just sold your duplex for $750,000 and are eyeing an enticing condominium building in an up-and-coming part of town for $1.5 million.
| Without 1031 Exchange | With 1031 Exchange | |
| Sale Price | $750,000 | $750,000 |
| Capital Gains Tax Rate | 37.1% | 0% (Deferred) |
| Capital Gains Tax Amount | $92,750 | $0 (Deferred) |
| Net Proceeds After Tax | $657,250 | $750,000 |
| Replacement Property Purchase Price | $1,500,000 | $1,500,00 |
| Remaining Funds Needed to Purchase Replacement Property | $842,750 | $750,000 |
As you can see, without using a 1031 exchange to purchase the replacement property, you would owe nearly $100,000 more in closing costs. That’s not an insignificant amount of money, and it could mean the difference between securing a mortgage or additional renovations to the building.
That’s because when you set up and successfully execute a 1031 exchange, you keep equity in your portfolio instead of forfeiting it to the IRS. While you are only deferring the taxes and will be expected to pay them later (when the property is sold without exchanging), there is currently no law or stipulation preventing you from using a 1031 exchange on the replacement property when that day comes.
If the idea of a 1031 exchange sounds like something that aligns with your investment goals, Canyon View Capital may be able to help.
Canyon View Capital Offers 1031 Exchange Investment Options for Investors
Now that you have a better idea of 1031 exchanges and the many nuances involved with these tax-deferral tools, you’ll likely want to explore the 1031 exchange investment options available to you.
Canyon View Capital may have a solution for investors who are ready to sell properties but no longer want to carry the burden of property management or are concerned about the complexities and timeframes associated with 1031 exchanges.
We have built a large portfolio of multifamily properties across the Mid-South and Midwest and want to allow you to exchange into one or multiple as Tenants in Common. This approach streamlines the identification process, alleviating the complexities often tied to 1031 exchanges. Moreover, it caters to investors seeking passive real estate income, allowing them to enjoy truly passive returns and the many tax benefits of 1031 exchanges and multifamily real estate without the burden of property management.
Canyon View Capital manages, owns, and operates real estate valued at over $1B2. Our buy-and-hold strategy, concentrated in America’s heartland, is designed to provide consistent investment returns.
Want to learn more about 1031 exchange investment options? Reach out today!

